Types of Plant Cells Educake: A Comprehensive Guide
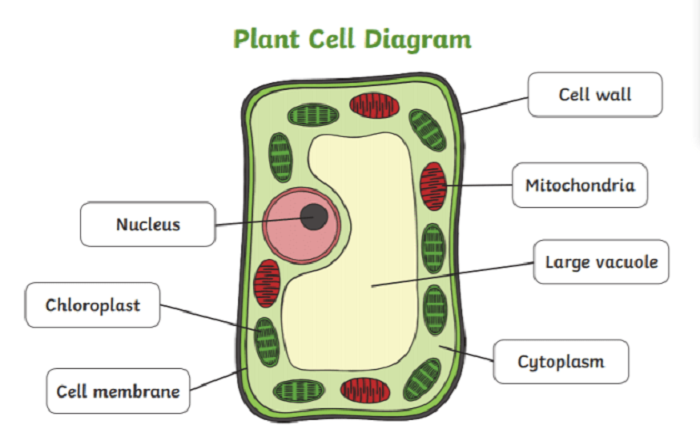
Understanding the types of plant cells Educake discusses is crucial for students studying plant biology. Plant cells have distinct structures and functions that contribute to the overall health and growth of plants. In this guide, we will delve into the various types of plant cells Educake highlights, their roles, and their significance in plant life.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Parenchyma Cells
One of the most common types of plant cells educake covers is parenchyma cells. These cells are essential for plant metabolism, including photosynthesis, storage, and repair. Parenchyma cells have thin walls and are usually found in the soft tissues of plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots.
The primary function of parenchyma cells is to support plant growth by storing nutrients and aiding in tissue regeneration. Educake explains how these cells play a vital role in healing plant wounds and assisting in plant development.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Collenchyma Cells
Another important type of plant cells Educake discusses is collenchyma cells. These cells provide structural support to growing plant parts, such as stems and leaves. Unlike parenchyma cells, collenchyma cells have thickened cell walls that offer flexibility and strength.
Educake explains how collenchyma cells allow plants to bend and withstand mechanical stress. Their unevenly thickened walls help young plants stay upright while allowing continued growth and expansion.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Sclerenchyma Cells
Among the types of plant cells Educake highlights, sclerenchyma cells are known for their toughness and durability. These cells have thick, lignified walls that provide immense strength and protection to plants.
Educake describes how sclerenchyma cells exist in two forms: fibers and sclereids. Fibers are elongated cells that add tensile strength to plants, while sclereids are shorter and contribute to the hardness of seed coats and nutshells.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Xylem Cells
Xylem cells are an essential type of plant cells Educake covers, responsible for water and nutrient transport within plants. Xylem tissue consists of tracheids and vessel elements, which work together to move water from roots to leaves.
Educake explains that xylem cells also provide structural support due to their thickened walls. These cells play a crucial role in maintaining plant hydration and nutrient distribution, ensuring overall plant survival.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Phloem Cells
Phloem cells are another key type of plant cells Educake explores, as they transport sugars and organic molecules throughout the plant. Phloem tissue consists of sieve tube elements and companion cells, which work together to distribute food produced during photosynthesis.
Educake emphasizes the importance of phloem cells in plant growth, development, and energy distribution. These cells function effectively by forming interconnected networks that help plants sustain themselves.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Epidermal Cells
Epidermal cells are a vital types of plant cells educake highlights as they form the outer protective layer of plants. These cells act as a barrier against water loss, pathogens, and environmental damage.
Educake explains how epidermal cells often produce a waxy cuticle that minimizes water loss. Some specialized epidermal cells, like guard cells, regulate gas exchange and transpiration through stomata.
Types of Plant Cells Educake: Meristematic Cells
The final type of plant cells Educake discusses is meristematic cells. These are undifferentiated cells responsible for plant growth and development. Meristematic cells are found in growing regions, such as root tips and shoot tips.
Educake highlights how these cells continuously divide, giving rise to new cells that differentiate into various plant tissues. They are essential for primary and secondary growth, ensuring the expansion and regeneration of plant structures.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of plant cells Educake explains is fundamental for grasping plant biology. From parenchyma and collenchyma cells to xylem and phloem, each type plays a crucial role in plant function and survival. By studying these plant cells, students gain insight into the complexity of plant life and their biological importance.
FAQs
1. What are the main types of plant cells Educake covers?
Educake covers parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, xylem, phloem, epidermal, and meristematic cells.
2. What is the function of xylem cells in plants?
Xylem cells transport water and nutrients from roots to leaves and provide structural support to the plant.
3. How do phloem cells differ from xylem cells?
Phloem cells transport sugars and nutrients, while xylem cells primarily move water and minerals throughout the plant.
4. Why are meristematic cells important in plant growth?
Meristematic cells are responsible for plant growth by continuously dividing and differentiating into specialized cell types.
5. What role do epidermal cells play in plants?
Epidermal cells form a protective barrier, prevent water loss, and regulate gas exchange through specialized structures like stomata.



